New Microsoft patent reveals human-like chatbots and conversational agents
By Abhishek Baxi · Sep 4, 2020
By Abhishek Baxi · Sep 4, 2020
[SHOWTOGROUPS=4,20,22]
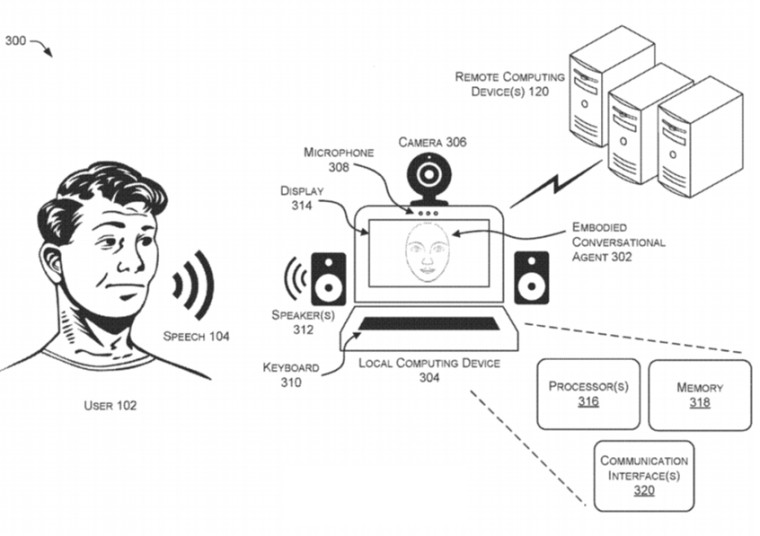
A new patent granted to Microsoft by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) reveals that the company is working on conversational agents that mirror users’ conversational style and/or facial expressions. The patent - Для просмотра ссылки Войдиили Зарегистрируйся – was granted to Microsoft on September 3, 2020, and credits Daniel J McDuff, Kael R. Rowan, Mary P Czerwinski, Deepali Aneja, and Rens Hoegen as inventors.
With advances in speech recognition and generative dialogue models, conversational interfaces like chatbots and virtual agents are becoming increasingly popular. While such natural language interactions have led to an evolution in human-computer interactions, the communication is mostly monotonic and constrained.
These conversations, therefore, end up being only transactional and are not very natural.
This new patented technology aims to bring an end-to-end voice-based conversational agent that can engage in a more natural, multi-turn dialogue that aligns with a user's conversational style and facial expressions.
[/SHOWTOGROUPS]

A new patent granted to Microsoft by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) reveals that the company is working on conversational agents that mirror users’ conversational style and/or facial expressions. The patent - Для просмотра ссылки Войди
With advances in speech recognition and generative dialogue models, conversational interfaces like chatbots and virtual agents are becoming increasingly popular. While such natural language interactions have led to an evolution in human-computer interactions, the communication is mostly monotonic and constrained.
These conversations, therefore, end up being only transactional and are not very natural.
This new patented technology aims to bring an end-to-end voice-based conversational agent that can engage in a more natural, multi-turn dialogue that aligns with a user's conversational style and facial expressions.
The conversational agent may be audio-only or embodied, meaning it has a ‘face’ which appears to speak. In both these implementations, the agent may use machine-learning techniques and respond to utterances from a user in a natural and understandable way, thereby improving human-machine interactions as a whole.A conversational agent that is implemented as a voice-only agent or embodied with a face may match the speech and facial expressions of a user. Linguistic style-matching by the conversational agent may be implemented by identifying prosodic characteristics of the user's speech and synthesizing speech for the virtual agent with the same or similar characteristics. The facial expressions of the user can be identified and mimicked by the face of an embodied conversational agent. Utterances by the virtual agent may be based on a combination of predetermined scripted responses and open-ended responses generated by machine learning techniques. A conversational agent that aligns with the conversational style and facial expressions of the user may be perceived as more trustworthy, easier to understand, and create a more natural human-machine interaction.
[/SHOWTOGROUPS]
