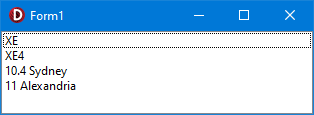
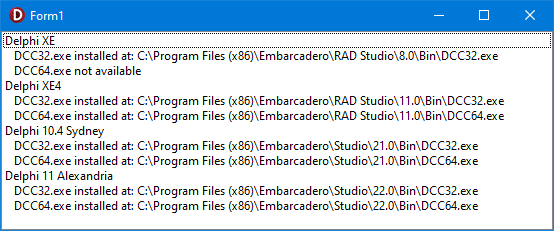
How to programatically detect installed versions of Delphi
Introduction
If you're wanting to execute Delphi or, more likely, its command line compiler from another application, you need a way of finding which Delphi versions are installed. You also need to know where the desired executables have been installed.The information we need to detect Delphi installations and to execute the compiler is recorded in the registry.
We will take this in two stages. First we will enumerate all installed versions of Delphi and then we will find the full path to an available command line compiler.
Actually executing the compiler from within your program, in a meaningful way, is beyond the scope of this article. If you want another article about how to do that, Для просмотра ссылки Войди
In the meatime, you can see some code that does this in my Для просмотра ссылки Войди
Note for users of older Delphi compilers: The example code in this article was written and tested in Delphi 11 Alexandria. The code uses features of the later Delphi compilers and will not compile on older version without change. In the main you may need to move all variable declarations out of the body of the code into a var section at the top of each routine. The code also uses for .. in loops quite extensively.
Find valid Delphi installations
Enumerate registry keys
First things first. Lets see where Delphi install information is stored in the registry. That depends on whether Delphi / RAD Studio was installed just for the current user or for all users of the machine.When installed for all users the information we want is under the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE root key, but if installation was for only the current user we need to look in HKEY_CURRENT_USER.
The path to the required data differs for each version of Delphi, but is the same for each root key. The format of the path has changed over the years as Delphi has evolved. The following table gives the registry paths for each version from Delphi 2 to Delphi 11 Alexandria:
| Delphi version | Registry path |
|---|---|
| 2 | \SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\2.0 |
| 3 | \SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\3.0 |
| 4 | \SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\4.0 |
| 5 | \SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\5.0 |
| 6 | \SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\6.0 |
| 7 | \SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\7.0 |
| 2005 | \SOFTWARE\Borland\BDS\3.0 |
| 2006 | \SOFTWARE\Borland\BDS\4.0 |
| 2007 | \SOFTWARE\Borland\BDS\5.0 |
| 2009 | \SOFTWARE\CodeGear\BDS\6.0 |
| 2010 | \SOFTWARE\CodeGear\BDS\7.0 |
| XE | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\8.0 |
| XE2 | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\9.0 |
| XE3 | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\10.0 |
| XE4 | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\11.0 |
| XE5 | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\12.0 |
| XE6 | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\14.0 |
| XE7 | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\15.0 |
| XE8 | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\16.0 |
| 10 Seattle | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\17.0 |
| 10.1 Berlin | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\18.0 |
| 10.2 Tokyo | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\19.0 |
| 10.3 Rio | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\20.0 |
| 10.4 Sydney | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\21.0 |
| 11 Alexandria | \Software\Embarcadero\BDS\22.0 |
Код:
uses
System.Win.Registry;
type
TDelphiInfo = record
Name: string;
RegKey: string;
end;
const
AllDelphis: array[0..24] of TDelphiInfo = (
(Name: '2'; RegKey: '\SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\2.0'),
(Name: '3'; RegKey: '\SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\3.0'),
(Name: '4'; RegKey: '\SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\4.0'),
(Name: '5'; RegKey: '\SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\5.0'),
(Name: '6'; RegKey: '\SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\6.0'),
(Name: '7'; RegKey: '\SOFTWARE\Borland\Delphi\7.0'),
(Name: '2005'; RegKey: '\SOFTWARE\Borland\BDS\3.0'),
(Name: '2006'; RegKey: '\SOFTWARE\Borland\BDS\4.0'),
(Name: '2007'; RegKey: '\SOFTWARE\Borland\BDS\5.0'),
(Name: '2009'; RegKey: '\SOFTWARE\CodeGear\BDS\6.0'),
(Name: '2010'; RegKey: '\SOFTWARE\CodeGear\BDS\7.0'),
(Name: 'XE'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\8.0'),
(Name: 'XE2'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\9.0'),
(Name: 'XE3'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\10.0'),
(Name: 'XE4'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\11.0'),
(Name: 'XE5'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\12.0'),
(Name: 'XE6'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\14.0'),
(Name: 'XE7'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\15.0'),
(Name: 'XE8'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\16.0'),
(Name: '10 Seattle'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\17.0'),
(Name: '10.1 Berlin'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\18.0'),
(Name: '10.2 Tokyo'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\19.0'),
(Name: '10.3 Rio'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\20.0'),
(Name: '10.4 Sydney'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\21.0'),
(Name: '11 Alexandria'; RegKey: '\Software\Embarcadero\BDS\22.0')
);
function IsRegisteredInRootKey(RootKey: HKEY; SubKey: string): Boolean;
begin
var Reg: TRegistry := TRegistry.Create(KEY_READ);
try
Reg.RootKey := RootKey;
Result := Reg.OpenKeyReadOnly(SubKey);
if Result then
Reg.CloseKey;
finally
Reg.Free;
end;
end;
function IsRegistered(SubKey: string): Boolean;
begin
Result := IsRegisteredInRootKey(HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, SubKey);
if not Result then
Result := IsRegisteredInRootKey(HKEY_CURRENT_USER, SubKey);
end;
function FindInstallations: TArray<TDelphiInfo>;
begin
SetLength(Result, Length(AllDelphis));
var FoundCount: Integer := 0;
for var Rec: TDelphiInfo in AllDelphis do
begin
if IsRegistered(Rec.RegKey) then
begin
Result[FoundCount] := Rec;
Inc(FoundCount);
end;
end;
SetLength(Result, FoundCount);
end;Here's how this works.
- TDelphiInfo and AllDelphis together form the table of records mentioned above that stores the required registry information for each compiler.
- FindInstallations checks the registry for every compiler in AllDelphis and returns an array of TDelphiInfo records for each compiler where its installation subkey is found in the registry. FindInstallations uses the IsRegistered helper routine to actually check the registry.
- IsRegistered checks for the given subkey in both the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE and HKEY_CURRENT_USER root keys. This is because Delphi can be installed for all users of a computer or for a specified user. In the former case the installation information is stored under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE and in the later case the information is stored under HKEY_CURRENT_USER.
- IsRegistered calls IsRegisteredInRootKey to check whether the given subkey is found in each root key.